Definition Of Buffer Capacity Of Soil
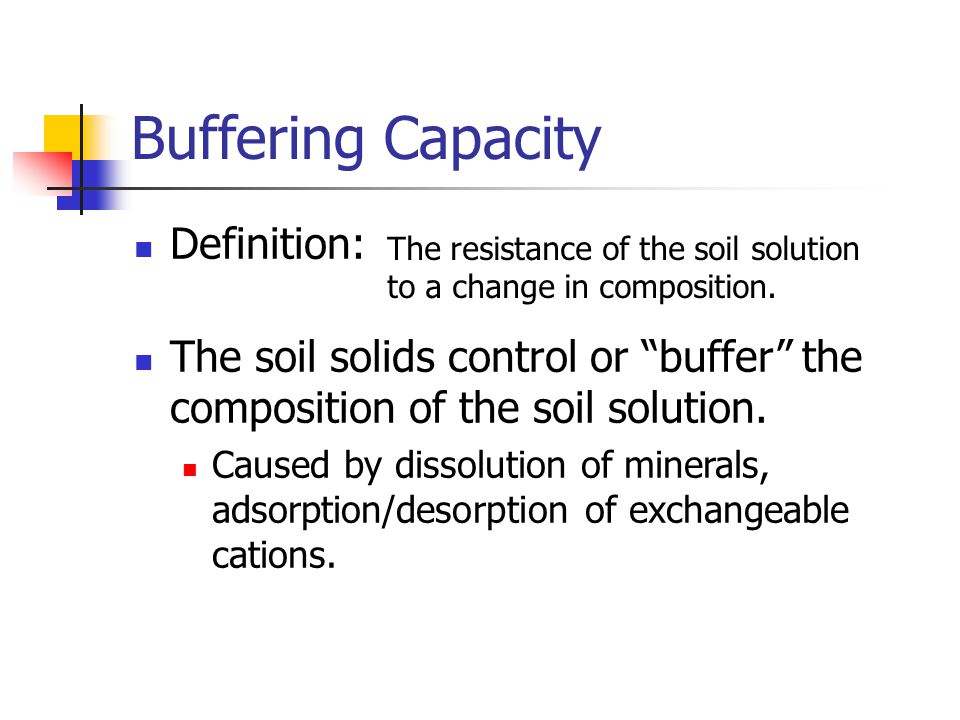
Buffering capacity is the ability of the soil to resist change. The buffer capacity of a soil is important in determining how its pH will change.
2 1 Soil Water Holding Capacity
The buffer capacity equation is as follows.

Definition of buffer capacity of soil. Buffer capacity A measure of the resistance of a buffer solution to pH change upon addition or removal of hydroxide ions. So to give a more clear definition buffer capacity may be defined as the quantity of a strong acid or strong base that must be added to one liter of a solution to change it by one pH unit. Organic matter content 3.
2012 Farlex Inc. Assuming a soil of low buffering capacity low clay and organic matter contents and as long as you apply it at rates that cover all of your crops nitrogen needs. As might be expected soil buffering depends on several factors.
A higher buffer capacity means that the soil can absorb more acid andor base without a significant change in pH. Cation exchange capacity CEC is a relative guideline which can help relate the. We studied i the pH buffer capacity pHBC of calcareous soils varied widely in calcite and texture ii the contribution of soil properties to pHBC and iii the significance of using a model based on calcite dissolution to estimate the pHBC of calcareous soils.
The higher the CEC the more cations which can be supplied. The pHBC is often quoted as a single value for a particular. Calculation of soil acidification rates requires knowledge of pH buffering capacity pHBC which is measured using titration methods.
PH measures the concentration of hydrogen ions in the soil solution. Thus aluminum and hydrogen of one pool will replenish the aluminum and hydrogen of another pool as these acid cations are removed. The buffering capacity of a soil indicates the capacity of the soil to resist pH change.
Clay content and type texture 2. Buffer Capacity and Percent Base Saturation Cations on the soils exchange sites serve as a source of resupply for those in soil water which were removed by plant roots or lost through leaching. This is called the soils buffer capacity.
Would ammonium sulfate do it. And when we talk of buffering. A buffer index can be calculated and then used to compute a lime rate needed to achieve a desired pH level.
Buffer capacity of soil is defined as a soils ability to maintain a constant pH level during action on it by an acidifier or alkalescent agent. A soil considered a mixture of buffered systems contains components which have the ability to neutralize acids by bonding H ions as well as bases by the release of hydrogen ions Federer and Hornbeck 1985. Soils differ in the number of surface sites able to accommodate hydrogen ions.
Buffering Capacity is the ability of the soil to re-supply an ion to the soil solution. So because of the tendency of the soil colloid either to adsorb H and Al 3 ions from soil solution or to give up those to the soil solution to maintain the equilibrium the soil tends to resist sudden changes in pH and this action is said to be the buffering action of the soil. Soil texture is also a major factor that controls how much water a soil can hold water holding capacity Figure 3 how available it is to plants available water capacity how good it is at holding onto lime or other nutrients buffer capacity and how well roots can grow.
Buffer capacity β is defined as the moles of an acid or base necessary to change the pH of a solution by 1 divided by the pH change and the volume of buffer in liters. Note that the addition of n moles of acid will change the pH by the same value but in the opposite direction. Dr Rao let us try to understand with the open mindset that soil buffering capacity is a comprehensive soil property which explains the behaviour of soil in totality.
In the case of acidity it is the ability of the soil to resist change in pH. Hydrogen ions in soil are present both in the soil solution and adsorbed onto the soil surfaces. I need to decrease soil pH from 73 to 63.
Where n is some equivalents of added strong base per 1 L of the solution. Soil buffering is the ability of the soil to stop nutrient or pH changes by absorption. Buffering capacity is an important property of soils.
A buffer resists changes in pH due to the addition of an acid or base though consumption of the buffer. The short-term buffering of soils is small around neutrality and increases in the alkaline and acid ranges. Buffer solution measures a given soils reserve acidity or buffering capacity.
In general clay soils have higher buffer capacity than sandy soils and a higher organic matter content tends to increase buffering capacity. Humic acids and clay minerals have good buffer qualities. Buffer index values for any given soil depend on the amount and type of clay and level of organic matter in that soil.
It is a unitless number. For soils it is the capability of absorbing nutrients and also releasing them cation exchange capacity. In chemistry buffer capacity is the amount of acid or base a buffered solution can soak up before its pH will start to change significantly.
 Pdf Soil Ph Buffering Capacity A Descriptive Function And Its Application To Some Acidic Tropical Soils
Pdf Soil Ph Buffering Capacity A Descriptive Function And Its Application To Some Acidic Tropical Soils
Http Lawr Ucdavis Edu Classes Ssc102 Section8 Pdf
Https Www Tandfonline Com Doi Pdf 10 1080 02571862 2009 10639961
 Proglottid Science Flashcards Science Facts Science Student
Proglottid Science Flashcards Science Facts Science Student
 Soil Chemical Properties Ppt Video Online Download
Soil Chemical Properties Ppt Video Online Download
 Buffer Capacity Video Buffer Solutions Khan Academy
Buffer Capacity Video Buffer Solutions Khan Academy
 Soil Ph Unit Soil Science Objectives O Define Acidity Alkalinity Buffering Capacity Soil Ph O List And Describe Inherent Factors That Affect Soil Ppt Download
Soil Ph Unit Soil Science Objectives O Define Acidity Alkalinity Buffering Capacity Soil Ph O List And Describe Inherent Factors That Affect Soil Ppt Download
 Soil Science Digitalis Tankonyvtar Soil Chemistry Lessons Agriculture Classroom
Soil Science Digitalis Tankonyvtar Soil Chemistry Lessons Agriculture Classroom
Https Hamilton Osu Edu Sites Hamilton Files Imce Soils 20general 20ver 204 27 2016 Pdf
 Cec Stuff To Internalize Or Project Onto Something Already Known Nrem Soils Soil Health Humus Soil Composting Process
Cec Stuff To Internalize Or Project Onto Something Already Known Nrem Soils Soil Health Humus Soil Composting Process
 Balance Soils Cation Exchange Soil Health Science Infographics Soil
Balance Soils Cation Exchange Soil Health Science Infographics Soil
 Calculating Cation Exchange Capacity Base Saturation And Calcium Saturation Ohioline
Calculating Cation Exchange Capacity Base Saturation And Calcium Saturation Ohioline
 5 Buffering Capacity Clay Minerals Sandy Soil Capacity
5 Buffering Capacity Clay Minerals Sandy Soil Capacity

Http Www The Macc Org Wp Content Uploads 2014 Soil Ph Buffering Pdf


