Ph Buffer Definition Biology
A buffer is selected on the basis of its pK a and its chemical nature. Define buffers and discuss the role they play in human biology The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14.
How To Choose The Perfect Buffer To Get A Pure Stabilised Functional Protein Tebu Bio S Blog
A buffer is an aqueous solution used to keep the pH of a solution nearly constant.
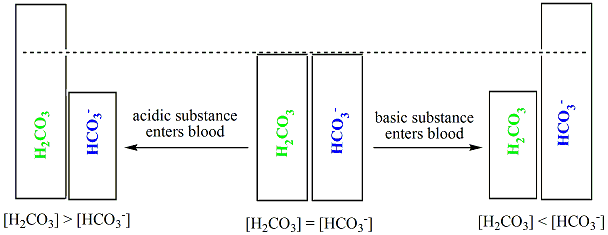
Ph buffer definition biology. The buffer helps to maintain a constant pH. Buffers are the mixture of weak acids and their salts of strong bases or the mixture of weak bases and their salts of strong acids. For instance one of the buffers that maintain the pH of human blood involves carbonic acid H.
Buffers help to maintain a normal pH of the biological systems. Biological buffers are compounds that help the body maintain a pH around 74. This solution is quite important in the field of chemistry.
PH -log a H where a H stands for hydrogen activity which is the effective concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. When an acid or alkali has added the pH of the solution changes in the absence of buffers. A buffer must contain the chemical species for neutralizing added amounts of acid or base.
Write the chemical equation. Buffer capacity is the amount of acid or base that can be added before the pH of a buffer changes. Adilah Anwar Jaya Barad Jacquelyn Calhoun and Sammi Chadrow Note that each question has multiple parts that must be answered.
A buffer consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. It is a water-based salt solution containing disodium hydrogen phosphate sodium chloride and in some formulations potassium chloride and potassium dihydrogen phosphate. Lab 4 Buffers and pH group assignment Names.
A buffer solution refers to an aqueous solution. Buffer solutions are used as a means of keeping pH at a nearly constant value in a wide variety of chemical applications. Buffers A buffer solution is one that resists a change in pH on the addition of acid H or base OH more effectively than an equal volume of water.
Phosphate-buffered saline abbreviated PBS is a buffer solution commonly used in biological research. The major urinary buffers are bicarbonate and phosphate buffers. 2 A molecule that serves to prevent large changes in pH by either combining with H or by releasing H into solution.
Parts A B in the prep notes water and pH 1 point Water Ionizes. Biological buffers are organic substances that maintain a constant pH over a given range by neutralizing the effects of hydrogen ions. A buffer is a chemical system designed to prevent dramatic alterations in fluid pH by binding up any changes in hydrogen ion concentrations due to excess acid or base production.
Note- A lot of biological chemical reactions need a constant pH for the reaction to proceed. The pH of a solution is a measure of its acidity or alkalinity base. Buffers are able to find any extra H or OH- ions and prevent pH change.
Buffer Chemistry 1 A chemical system that minimises the effectsin particular the pHof changes in the concentration of a substance. DEFINITION A buffer is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid its salt or a weak base its salt that resist a change in pH on the addition of either acid or base. You can explore more about buffer solutions here.
As the filtrate proceeds along the tubules the ratio between base member and the acid member of each urinary buffer falls progressively with a consequent fall in the urinary pH. Make room between questions. Relate this concept to pH.
Most buffers consist of a weak acid and a weak base. A buffer by definition resists changes in the pH of the solution. Buffers typically consist of an acid-base pair with the acid and base differing by the presence or absence of a proton a conjugate acid-base pair.
OH 2 H 2 O H 3 O Kw is the. Essentially the definition uses the equation. Maintenance of biological pH is important because cells only function over a narrow pH change.
A buffer solution more precisely pH buffer or hydrogen ion buffer is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versa. Furthermore it consists of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice-versa. The urinary pH is maintained by a cooperation between the urinary buffers and the renal ion-exchange mechanism.
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry IUPAC has a slightly different pH scale that is based on electrochemical measurements of a standard buffer solution. Generally a buffer is a solution of a weak acid and its conjugate base eg ammonia and ammonium chloride. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it.
Buffers are commonly used in research labs especially in applications involving protein electrophoresis polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting.
 Trick To Find The Ph Of A Buffer Solution Class 11 Chemical Equilibrium Youtube In 2020 Buffer Solution Solutions Chemical
Trick To Find The Ph Of A Buffer Solution Class 11 Chemical Equilibrium Youtube In 2020 Buffer Solution Solutions Chemical
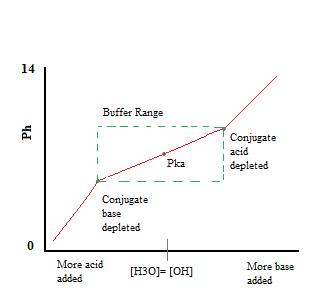 Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
 Buffers Definition Overview Expii
Buffers Definition Overview Expii
 Effect Of Ph On Enzymatic Activity Enzymes Activity Biochemistry Enzymes
Effect Of Ph On Enzymatic Activity Enzymes Activity Biochemistry Enzymes
 Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Solutions Electron Configuration
Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Solutions Electron Configuration
 Buffer Capacity Buffers Titrations And Solubility Equilibria Chemi Solubility Chemistry Ap Chemistry
Buffer Capacity Buffers Titrations And Solubility Equilibria Chemi Solubility Chemistry Ap Chemistry
 Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
 Ph Poh H3o Oh Kw Ka Kb Pka And Pkb Basic Calculations Acids And Bases Chemistry Problems You Chemistry Basics Chemistry Lessons Teaching Chemistry
Ph Poh H3o Oh Kw Ka Kb Pka And Pkb Basic Calculations Acids And Bases Chemistry Problems You Chemistry Basics Chemistry Lessons Teaching Chemistry
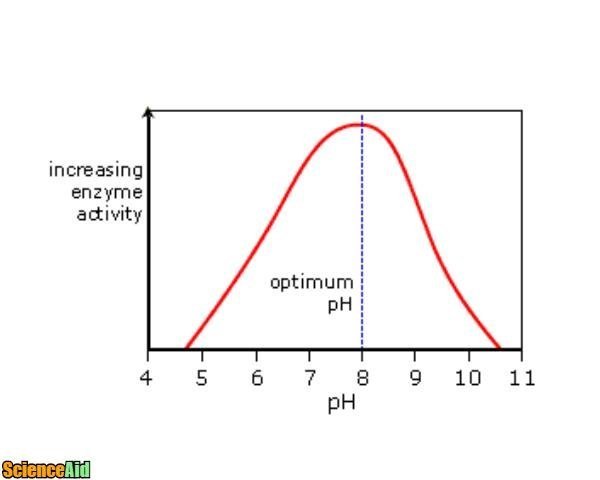 Enzymatic Activity And Ph Buffers Scienceaid
Enzymatic Activity And Ph Buffers Scienceaid
Ph Buffers Acids And Bases Introduction To Chemistry
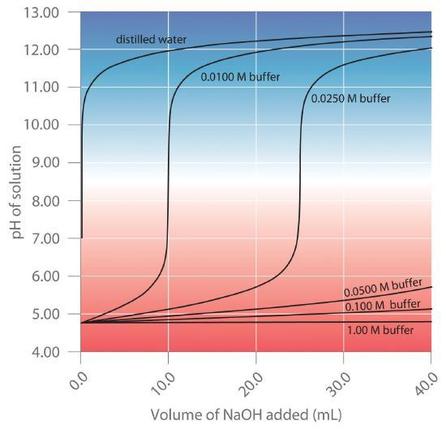 8 9 Buffer Capacity And Buffer Range Chemistry Libretexts
8 9 Buffer Capacity And Buffer Range Chemistry Libretexts
 The Ph Scale Universal Indicator Ph Color Chart Diagram Acidic Alkaline Values Common Substances Vector I Human Body Systems Medical Knowledge Science For Kids
The Ph Scale Universal Indicator Ph Color Chart Diagram Acidic Alkaline Values Common Substances Vector I Human Body Systems Medical Knowledge Science For Kids
 Bicarbonate Buffer System Example Of Multiple Equilibria Teaching Chemistry Medical School Studying Biochemistry
Bicarbonate Buffer System Example Of Multiple Equilibria Teaching Chemistry Medical School Studying Biochemistry
 Ph Chart For Acids And Bases Ph Chart Study Chemistry Electron Configuration
Ph Chart For Acids And Bases Ph Chart Study Chemistry Electron Configuration
 Chemistry Of Buffers And Buffers In Our Blood Article Khan Academy
Chemistry Of Buffers And Buffers In Our Blood Article Khan Academy



